

React Native and Flutter are today’s most popular cross-platform mobile app development frameworks. While React Native has been around for a few years, Flutter is relatively new and released in May 2017. So the big question on every developer’s mind is: Which one should you use?
In this post, we’ll compare React Native and Flutter, examining their various features and strengths. In conclusion, you should have a good sense of which platform is best for your next project.
What is React Native?
Facebook developed React Native, which is a cross-platform mobile development toolkit. It allows you to use React and native platform capabilities to create iOS and Android apps. React Native uses the same fundamental UI building blocks as regular react for web development, Making it more accessible for JavaScript developers to break into the field. This makes it much easier for developers who are already familiar with React to get started with React Native.
At this point, React Native v0.69 has been released, which includes opt-in support for the new React Native architecture using the Fabric Renderer and TurboModule framework. Because no libraries have yet migrated to the new architecture, it’s opt-in only.
The Fabric Renderer adds concurrent rendering, React Suspense, and server-side rendering to React Native, as well as a more interoperable toolset.
REACT NATIVE: PROS AND CONS
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Because it is based on JavaScript language, React Native has good community support | Native developers are still required |
| A single codebase allows developers to develop apps for many devices simultaneously rather than one at a time | Performance is poor in comparison to Flutter |
| It allows for code reuse, cost-cutting, and rapid app development | Debugging issues |
| Relatively maturity | There are fewer components to assemble out of the box |
| There is a large and active community | There are a lot of unneeded packages and libraries |
| It’s simple for React developers to pick up | UI is delicate |
| Apps are generally larger than native applications |
What is Flutter?
Google created Flutter, a multi-platform user interface (UI) framework. Flutter has been around since May 2017, but it has seen steady popularity growth.
Flutter’s most prominent selling point is that it allows you to write cross-platform apps with a single codebase. Traditionally, a company needed several tools and developers to build a web, mobile, or desktop application. But with Flutter, you can use a single codebase to create all three. This makes development much faster and easier.
Flutter is still in its early stages, but it has already seen adoption by some big companies, including Alibaba, Capital One, and Google.
Flutter 3 introduced several significant changes. Using the same codebase, you may now develop iPhone, Android, Web, Windows, Mac, and Linux apps using the Flutter Compiler. Flutter 3 also adds new features, including better integration between Firebase and Flutter and a Casual Games Toolkit for making games with Flutter.
FLUTTER: PROS AND CONS
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Using the same codebase, you can rapidly develop | As flutter is new, you’ll encounter several typical issues that aren’t simple to fix |
| “Hot Reload” allows you to test and fix issues quickly | Apps take longer to install and consume a lot of space |
| The layered architecture allows for greater customization and control | Programming language (Dart) and framework that is continuously updated |
| Excellent documentation | However, the libraries and support are not as productive as native development |
| Errors are prevented by having a separate user interface | |
| User-friendly interfaces |
Now that we’ve looked at each platform individually let’s compare them side-by-side.
Which one is the best fit for your app?
| Choose Flutter | Choose React Native |
|---|---|
| When your app will put a significant strain on the CPU and GPU | The app will exclusively make use of native visual components |
| A lot of time will be spent on the user interface’s customization | Your development team is trained in JavaScript and React |
| Wearable and embedded devices will be targeted | The app is solely available online or on mobile devices (iOS, Android) |
Main differences between Flutter and React Native?
There are several similarities and differences between Flutter and React Native. The most significant difference is that React Native uses JavaScript while Flutter uses Dart.
Dart is a typed language that can catch errors at compile time instead of runtime. This makes development faster and easier. Dart also has better support for type inference, making it easier to write less error-prone code.
React Native is more popular than Flutter, meaning more libraries and resources are available for React Native. However, Flutter is growing quickly and is catching up to React Native in terms of popularity.
Both languages are object-oriented. In terms of design, Flutter and React Native are essentially the same, with similar code.
Comparison of Flutter and React Native
We’ve put up a simple table for you to evaluate the two alternatives:
| Technology | React Native | Flutter |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Language | Javascript | Dart |
| Components Library | Large, inclusive | smaller, non-inclusive |
| Performance | Because of JavaScript bridging, the app may take longer to load | High-performing and fast |
| Adaptive Components | Some are adaptive on their own | Components can’t be adaptive. You must configure them manually |
| Learning Curve | It’s simple to get started with, especially if you’re used to working on React or Javascript | It’s quite steep; you’ll need to grab Dart, and reactive programming isn’t always easy |
| Created By | ||
| Main Architecture | Flux and Redux | BLoC |
| EcoSystem | Quite Mature, used in production in many large companies around the world, many different packages available | A fewer number of packages, not yet mature |
| Hot Reload | Supported | Supported |
| First Release | Jan 2015 | May 2017 |
Development experience and tools
Both Flutter and React Native come with excellent development tools.
Flutter’s Dart plugin has excellent analysis capabilities. It can help you find dead code, identify potential errors, and optimize your code.
React Native also has a great set of development tools. The React Native debugger is powerful and can help you quickly find and fix bugs.
React Native and Flutter Demand
As a result, there is currently a greater demand for React Native developers than for Flutter ones. However, Flutter isn’t any less popular; instead, it has been gaining in popularity over time.
React Native and Flutter Performance
It’s challenging to determine which Flutter or React Native app is superior in terms of performance. It will not be the same for every app; many factors, such as the type of app, codebase, animations, transitions, app size, layout, data passing, end user’s phone, and more.
Flutter and React Native is open source, which means you may use them for free. Because Google and Facebook develop them, you’d expect them to be well-maintained.
You may use the built-in simulator on your computer for iOS and Android, as well as an actual device, to test apps developed using either framework.
Hot reloading is used in both frameworks, which makes development more efficient since you may see the modifications instantly.
When it comes to user experience, your interaction with an application created in React Native and Flutter is primarily a native one. React Native works with native code through JavaScript bridges. Bridges might slow down the performance of an app.
The Flutter code, on the other hand, compiles directly to C, which is as close to native as it gets. Flutter does not require any bridges to communicate with native code. That’s something you can safely assume would result in improved performance.
React Native’s new architecture solved the performance problem by eliminating JavaScript bridges and favoring a JavaScript Interface (JSI). With the JSI, you may call your native module directly rather than using a bridge. The new React Native architecture also includes lazy-loading native modules via TurboModules, which may help to reduce the app load time.
With their developer and community support, Flutter and React Native is continuing to improve. However, regarding performance, Flutter has a slight edge over React Native.
React Native Architecture
Some of the commonly used architecture in React Native are :
- Flux Architecture
- Model View Controller Architecture
- Redux Architecture
Redux Architecture:
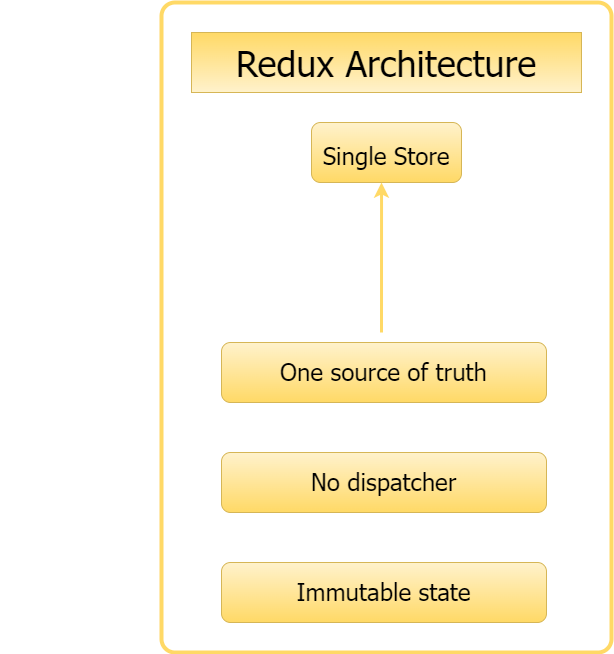
Redux is a JavaScript library that helps you manage application states. The Flux architecture was the source of inspiration for Redux. It’s essentially a flux-like way to build React applications.
Redux isn’t only for React, and it’s not necessary to use it with just that. It can also be used with AngularJS or JS. However, Redux works well with React. Redux allows you to manage the store, unidirectional data flow, and more.
Flux architecture has several stores linked together by the dispatcher, and when something changes, all stores must be updated. However, Redux only has a single store that handles the entire application. A change to the store is made using an action.
Now, we have reducer functions in Redux. These functions take the previous state of the application, and the action specified and produce the next state for the application. Redux’s state changes can only be made via these reducer functions. The previous state is kept, and a new one is generated.
Use of Redux:
- A Single Source: Redux only has one store, making it very easy to understand.
- Reducer Functions: These functions create a new state from the previous one, allowing you to connect all your conditions.
- Undo & Redo: As you walk back, you can always modify or update the states as needed.
- Time-travel was debugging: It’s possible always to go back and inspect your changes in Redux. State logging is simple.
- Use of JS: The action is defined in the reducer function and the previous state. The Payload of a JavaScript Object is referred to as an Action.
- Immutability: When a new state is created, the old state remains as it is and is not modified in any way.
Flutter Architecture
What is BLoC?
The Business Logic Component (BLoC) is an architectural pattern based on separate components (BLoC components). The BLoC components are solely used for business logic and can be easily shared across different Dart applications. Google introduced this architecture at Google I/O 2019. The current most popular Flutter architecture is the BLoC approach.
Why BLoC?
The separation of the business logic and the presentation layer is more straightforward with BLoC. The program becomes fast, simple to test, and reusable. A Flutter developer always wants to:
- Knowing what state my application is in at any given moment
- Develop efficient and fast apps that can respond to changes quickly
- It’s a simple process to test each case to ensure that my app responds correctly
- Many developers work in a single code base, utilizing the same patterns and standards
- Every action that a user takes within my application is recorded to help me make data-driven judgments
BLoC makes managing stateful widgets easier. Typically in React Native, developers utilize setState several times to achieve their goals. This starts to rebuild and causes performance issues. However, by using bloc classes, BLoC defines the business logic differently. This eliminates multiple rebuilds and improves performance.
BLoC apps are more testable since the logic and widgets are separated. Because of this, code also becomes more reusable since you may use the same logic in multiple places rather than developing it from scratch.
The BLoC architecture is quite basic and elegant, making it simple to understand for both junior and experienced developers that provide Flutter app development experts. The ability to create complex apps from smaller components is what makes the BLoC design so effective. While these small components are individual, it’s also simple to evaluate any aspect of an application.
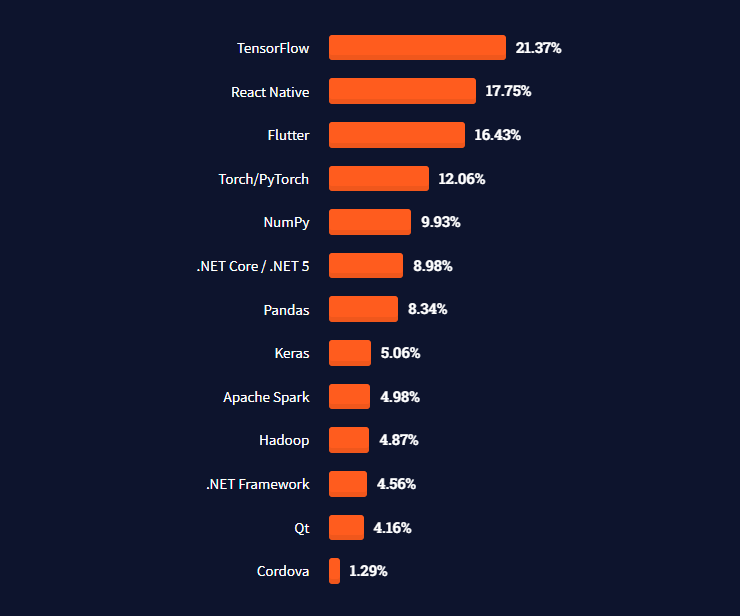
Most Loved and Wanted by Developers
Summery
- Flutter is a mobile app development platform that uses Dart, while React Native uses JavaScript.
- React Native has pros and cons but is generally a good choice for rapid app development.
- Flutter’s pros include “Hot Reload,” which allows for easy testing and bug fixing, while its cons include the fact that it is new. Thus you may encounter some issues that are difficult to fix, as well as the programming language (Dart) being updated often.
- However, each framework has benefits and drawbacks, with no significant difference in performance. They offer features like hot reloading, which makes development more efficient since you can see modifications instantaneously; however, this isn’t true for every app as some factors will determine how fast an application runs on either system (such as type/codebase).
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

